Selecting stadium lighting with inadequate heat dissipation poses significant risks. Poorly managed heat can lead to ignition of nearby materials like bird nests or lamp fixtures. This article discusses the importance of effective heat sink design in LED lights and provides guidance on identifying and avoiding low-quality products prone to such issues.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Heat is Managed Inside LED Chips?
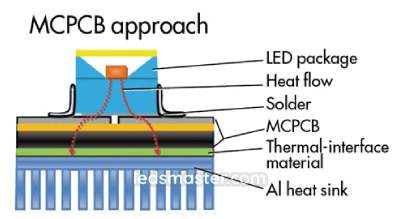 Heat generated by LED chips is transferred through the aluminum heat sink using soldering and other interface materials. Poorly designed components or manufacturing flaws can disrupt this process, leading to heat accumulation within the LED package and potential overheating that can damage the chips.
Heat generated by LED chips is transferred through the aluminum heat sink using soldering and other interface materials. Poorly designed components or manufacturing flaws can disrupt this process, leading to heat accumulation within the LED package and potential overheating that can damage the chips.
Effective heat sinks are crucial, providing ample surface area to dissipate heat into the surroundings. Some flood lamps have caught fire due to underestimating heat generation and using inadequately designed heat sinks. When purchasing stadium lights, it’s vital to exercise caution and avoid products with these potential risks.
Understanding Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how quickly materials conduct heat, typically in watts per meter kelvin (W/m·K). The table below summarizes the thermal conductivity values of various materials.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
| Diamond | 1000 |
| Silver | 406 |
| Copper (Pure) | 385 |
| Yellow Brass | 115 |
| Copper Brass (Copper 70% + Zirconium 30%) | 111 |
| Copper Bronze (Copper 75% + Tin 25%) | 26 |
| Gold | 315 |
| Aluminum | 205 |
| Magnesium | 159 |
| Zinc | 116 |
| Iron | 79.5 |
| Tin | 65 |
| Stainless Steel | 45 |
Copper alloy, aluminum, and tin are commonly used interface materials between the LED package and heat sink in the LED lighting industry. While materials like diamond and silver have significantly higher thermal conductivity (1000 and 406 W/mK respectively), their cost is prohibitively high, making them impractical for lamp production. If someone claims to have a material with a “superconducting” thermal conductivity of 200,000 to 300,000 W/mK or more, they would undoubtedly be deserving of a Nobel Prize.
What are Shoddy Stadium Lights?
 In recent years, the popularity of LED lighting for stadium illumination has grown exponentially, offering energy efficiency, longevity, and enhanced lighting quality. However, not all LED stadium lights are created equal. There have been instances where poorly designed lights have posed fire risks, highlighting the importance of selecting high-quality products for safety and reliability.
In recent years, the popularity of LED lighting for stadium illumination has grown exponentially, offering energy efficiency, longevity, and enhanced lighting quality. However, not all LED stadium lights are created equal. There have been instances where poorly designed lights have posed fire risks, highlighting the importance of selecting high-quality products for safety and reliability.
Understanding the Risks
The primary risk associated with shoddy LED stadium lights is their inadequate heat dissipation capability. LED lights generate heat during operation, and if this heat is not effectively managed and dissipated, it can lead to overheating. This overheating can potentially ignite surrounding materials such as bird nests, debris, or the lighting fixtures themselves. Such incidents not only endanger the structure and occupants but also undermine the investment made in lighting infrastructure.
Identifying Shoddy LED Stadium Lights
To avoid the pitfalls of substandard LED stadium lights, it’s crucial to be vigilant when selecting products. Here are key indicators to help identify shoddy lights:
Heat Dissipation Design
Effective LED stadium lights incorporate well-designed heat sinks that maximize surface area for heat dissipation. Materials like aluminum, known for their excellent thermal conductivity, are commonly used in quality heat sinks. Conversely, poorly designed heat sinks or the use of inadequate materials can impede heat transfer, increasing the risk of overheating and fire.
Build Quality
Thoroughly examine the overall build quality of the LED stadium lights. Look for signs of robust construction, such as sturdy housing, secure connections, and proper sealing against environmental factors. Lights with inferior build quality, such as loose components or flimsy materials, are more prone to malfunctions that could lead to overheating and safety hazards.
Certifications and Standards
Prioritize LED stadium lights that comply with recognized safety certifications and standards. Certifications from organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or ETL (Intertek) indicate that the lights have undergone rigorous testing for safety, reliability, and compliance with electrical codes. Such certifications offer assurance that the product meets essential safety criteria.
Manufacturer Reputation
Research the reputation and track record of the manufacturer. Established brands with a history of producing reliable lighting solutions are more likely to prioritize quality control and adhere to stringent safety standards in their products. A reputable manufacturer’s commitment to excellence extends to design, manufacturing processes, and customer support, ensuring higher product reliability and safety.
User Reviews and Feedback
Consult reviews and feedback from other users and industry professionals who have experience with the LED stadium lights you’re considering. User testimonials can provide valuable insights into real-world performance, reliability, durability, and any safety concerns that may not be apparent from technical specifications alone. Pay attention to recurring issues or positive endorsements regarding the product’s overall quality and safety features.
Conclusion
Safety is paramount, particularly in environments where lights operate at high temperatures. By prioritizing effective heat dissipation, robust build quality, adherence to safety standards, reputable manufacturers, and informed user feedback, stakeholders can mitigate risks and ensure the long-term safety and reliability of stadium lighting installations. Choosing wisely not only safeguards against fire hazards but also enhances the overall efficiency and sustainability of stadium lighting systems, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable experience for all.

